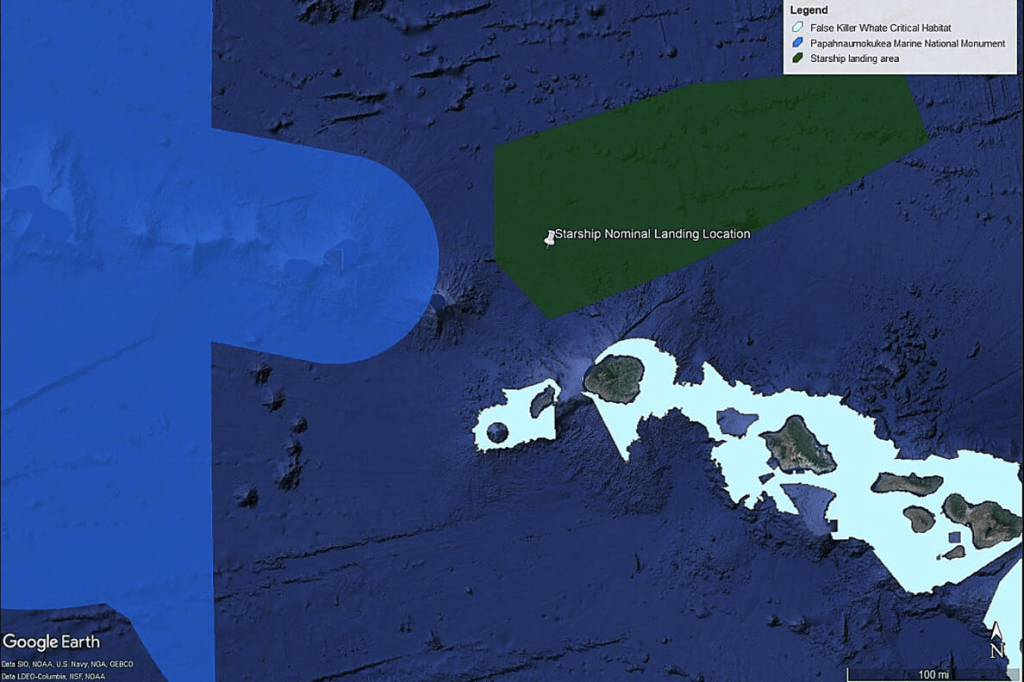
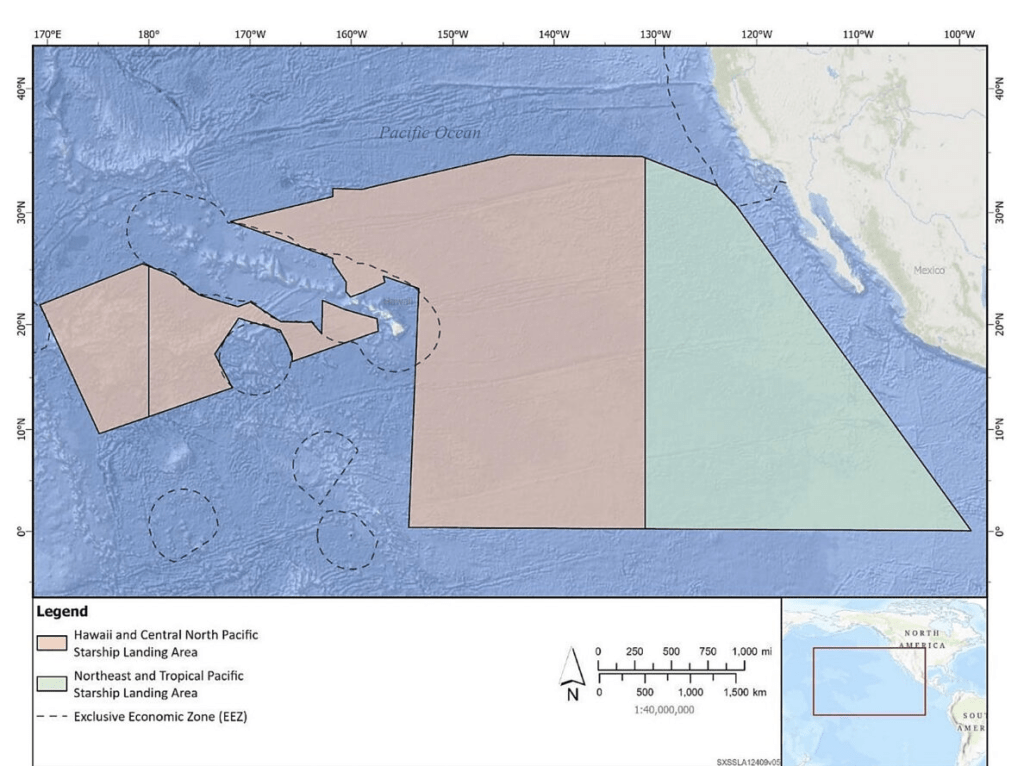
Reports from the public after launches or re-entries from SpaceX at Boca Chica, Texas, and Vandenberg AFB, California, compare the sound to an explosion, which also shatters windows and cracks concrete. These are not traditional “sonic booms.”
This rocket debris could have killed people or animals or caused a catastrophic fire. Notice the BCC’s language which makes light of the incident and the residents. 1 in 10,000 risk or worse is not a freak accident.
From the BBC
How a freak space junk crash baffled residents and sparked concern
Waihiga Mwaura
BBC Focus on Africa TV, Mukuku village
1-11-25
An eerie whizzing sound followed by a big boom startled Kenyan villagers relaxing recently one afternoon with family and friends.
“It sounded like a bomb, I was shocked. I started looking around, also wondering if it was gunshots,” Stephen Mangoka, a 75-year-old farmer from Makueni county’s Mukuku village, told the BBC.
“I looked up in the sky to see if there was smoke. Nothing.
“I rushed to the road to check if there had been an accident. Also, nothing. That is when someone told me that something had fallen from the skies.”
In fact, a massive round metal object had plummeted from above landing on farmland near a dry riverbed – and it was piping hot.
“We found a big piece of metal that was very red so we had to wait for it to cool before anyone could approach it,” said Ann Kanuna, who told us she owns the land where the object fell.
The giant ring took around two hours to cool down and turn grey – but it had already become a sensation with people arriving to look at it.
The rest of that Monday afternoon – with few people working as it was the day before New Year’s Eve – crowds came to view the giant metallic ring.
It was like selfie central, with people coming to pose next to it and great debates about what it could be.
The local authorities in Makueni county – which is around 115km (70 miles) south-east of the capital, Nairobi – were informed.
The Kenya Space Agency (KSA) then heard about it and made arrangements to come and investigate the next day.
But such was the object’s fame that Mukuku villagers feared it would be stolen overnight.
Together with local officers, some of them took it in turns to stand guard, lighting a fire nearby. They wanted to keep away potential scrap dealers and others wanting to make money out of the curiosity.
It is said to weigh more than 500kg (1,102lb) – around the same as an adult horse – and is around 2.5m (8ft) in diameter, roughly the size of child’s four-seater merry-go-round.
With daylight came more onlookers on New Year’s Eve – followed by the KSA team and the media.
Mukuku had never seen such activity. When the object was carted away later that day by the KSA, the buzz gave way to concerns about what the villagers had had in their midst.
The KSA said its preliminary assessments indicated the object was “a separation ring” from a space launch rocket.
“Such objects are usually designed to burn up as they re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere or to fall over unoccupied areas, such as the oceans,” its statement said the next day.
No-one was injured when it had fallen but some in Mukuku began to complain that the impact of the crash had caused damage to nearby houses.
Christine Kionga, who lives about a kilometre from the crash site, showed us cracks in the concrete of some of the buildings in her home compound. She said they had appeared after the crash.
Other neighbours alleged the structural integrity of their homes had also been affected – allegations that are yet to be substantiated.
“The government needs to find the owners of this object, and get compensation for those affected by it,” Mukuku resident Benson Mutuku told the BBC.
There were reports in the local media that some residents had begun to complain of feeling unwell after exposure to the metallic ring though there was no confirmation from those we spoke to when we visited – nor from the authorities or the KSA.
Nonetheless Mr Mutuku said there were concerns about the long-term effects of possible space radiation.
“This is a space object and we have heard in other similar incidents that there have been effects of radiation affecting even future generations and there is that fear in this community.”
However tests run later by the Kenya Nuclear Regulatory Authority revealed that while the metal ring did have higher radiation levels than the area in which it was found, they were not at a level harmful to humans.
Engineers from the KSA, which was established in 2017 to promote, co-ordinate and regulate space-related activities in the East African nation, are continuing to run other tests to find out more about the object.
The KSA director general said it was lucky that no significant damage was done when the object hurtled to Earth.
“The ultimate responsibility for any damage or injury caused by that space object is on the state in whose jurisdiction that operator may have launched the object,” Brigadier Hillary Kipkosgey told the BBC.
According to the Outer Space Treaty, overseen by the UN Office for Outer Space Affairs, “states shall be liable for damage caused by their space objects”.
“[The ring] is a common item in many rockets and many space objects so it difficult to attribute it to a specific rocket or space object but we have leads but as I said our investigations are not conclusive,” Brigadier Kipkosgey said.
The BBC showed pictures of the object to the UK Space Agency to get the thoughts of its experts.
“The most plausible object it could be is the upper stage separation ring from an Ariane rocket in 2008,” its launch director, Matt Archer, said.
“The satellites are fine, but the actual rocket body has come through and de-orbited.”
The Ariane was Europe’s main rocket launch vehicle, helping more than 230 satellites into orbit, before it was retired in 2023.
It seems the separation ring may have been orbiting Earth for 16 years before making its unexpected appearance in Mukuku.
This is not the first incident of space junk appearing in East Africa.
Just over a year and a half ago some suspected space debris fell over several villages in western Uganda.
And a few days ago, on 8 January, there were unconfirmed reports of what was believed to be space debris burning brightly in the skies above northern Kenya and southern Ethiopia.
As the space industry grows, it is predicted that such incidents will become more frequent – and African governments may need to invest in ways to better detect this speeding space rubbish.
Nasa estimates there are more than 6,000 tonnes of space debris in orbit at the moment.
There are many different estimates about the chances of such junk hitting someone, but most are in the one-in-10,000 range.
Such statistics are little comfort for Mukuku’s residents, who cannot help thinking of what damage the ring could have caused had it landed in the centre of the village instead of on farmland.
“We need assurances from the government that it won’t happen again,” said Mr Mutuku.
Captions:
The rocket ring fell not far from the centre of Mukuku village
The space junk fell just before new year celebrations